Lean Six Sigma is a method that relies on a collaborative team effort to improve performance by systematically removing waste and reducing variation. It combines lean manufacturing/lean enterprise and Six Sigma to eliminate the eight kinds of waste (muda): Defects, Over-Production, Waiting, Non-Utilized Talent, Transportation, Inventory, Motion, and Extra-Processing.
Lean Six Sigma not only reduces process defects and waste, but also provides a framework for overall organizational culture change. By introducing Lean Six Sigma, the mindset of employees and managers change to one that focuses on growth and continuous improvement through process optimization. This change in culture and the mindset of an organization maximizes efficiency and increases profitability.
What is LEAN?
Lean is often discussed as a mind-set or philosophy and its emphasis on systems thinking, team work and collaborative problem solving seeks to engage the entire workforce for the development of a culture of continuous improvement. The application of Lean principles facilitates the implementation of significant process improvements without the requirement for a thorough understanding of the underlying process. However, this lack of depth of understanding may well contribute to regression to old practices as observed for the majority of Lean initiatives. Furthermore, Anthony et al (2003) claims that the lack of a clear structure around Lean improvement initiatives constrains the potential scope and size of the improvement delivered.
The origin of Lean thinking is attributed to the Toyota Production System (TPS) and was popularised in the western business lore by the books ‘The machine that changed the world’ and ‘Lean Thinking’. The central tenet of Lean thinking is the elimination of waste, where waste is defined as anything that increases cost without adding value for the customer. The five principles underpinning this concept are: 1) value; 2) value stream; 3) flow; 4) pull; and 5) perfection. Lean’s focus on eliminating waste and improving flow has positive effects for product quality as the simplification of processes leads to reduced variation.
What is SIX SIGMA?
Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects (driving toward six standard deviations between the mean and the nearest specification limit) in any process – from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service.
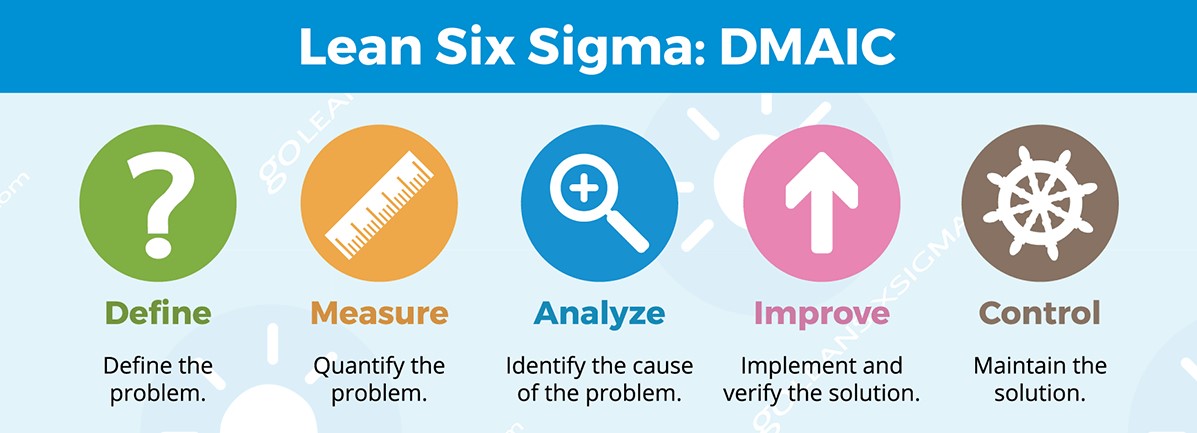
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects. This is accomplished through the use of two Six Sigma sub-methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV.
The Six Sigma DMAIC process (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) is an improvement system for existing processes falling below specification and looking for incremental improvement.